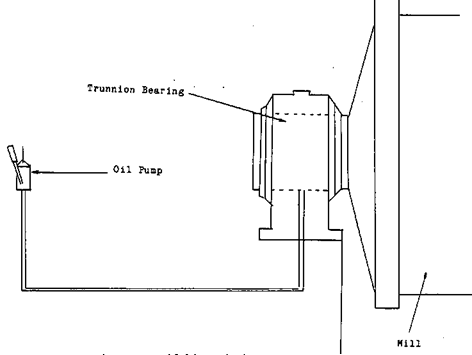
Bearings that interest us are in 3 categories: Hydrodynamic, Hydrostatic, and Roller.
Hydrodynamic and the hydrostatic make use of a phenomenon called the Wedge Effect. This wedge effect is a self-generated pressure that is developed when a film of oil between a moving shaft and a collar or sleeve is forced through a wedge shaped passage. This pressure is high enough to support the load on the shaft.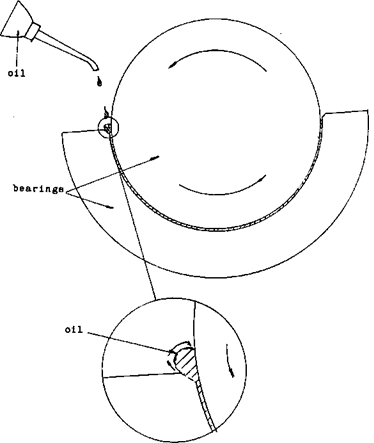
The difference between these Hydrodynamic and the hydrostatic type bearings lie in the work that they do. The first, hydrodynamic bearings are Slider Bearings and Journals. Slider bearings usually have two surfaces that slide across one another. Journal bearings are the type that are found in the engine of your car. They are the ones that are between the crankshaft and the connecting rods.
Hydrostatic bearings are slow turning and support a heavy load. When this type of bearing isn’t turning, the weight of the machine will squeeze the oil out from between the two bearing surfaces. Without special care this type of bearing can be damaged on start-up.
To guard against this, a pumping system is used to force the oil in between the two bearing surfaces. Once the machine is started and the RPM of the bearing is sufficient for the wedge effect to take place the pump may be shut off.
The two different types of bearings, the hydrostatic and the hydrodynamic, are often as not, constructed of what is known as BABBITTS METAL. Named after Isaac Babbitt, who obtained the patent on the bonding of alloys to a strong backing material to form bearings of what is sometimes referred to as anti-friction metals.
These bearings are made from one of the base metals tin, lead, or cadmium. They are combined with a combination of antimony, copper, arsenic, cadmium, or nickel in different proportions and combinations depending upon which characteristics are required.
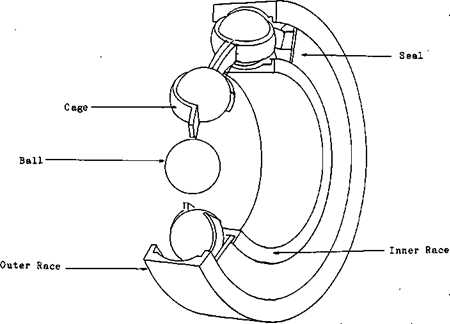
The roller bearing consists of four main parts, The INNER RING or RACE, THE OUTER RACE, the ROLLER or BALL, and the CAGE.
The roller portion of the hearing may be a hall or a cylindrical roller. The shape of the cylindrical roller will depend upon where and how it is used. It is the movement of these balls or rollers within their cage that reduce friction.
Now for the practical portion of this section, the bearings must be checked for heat.